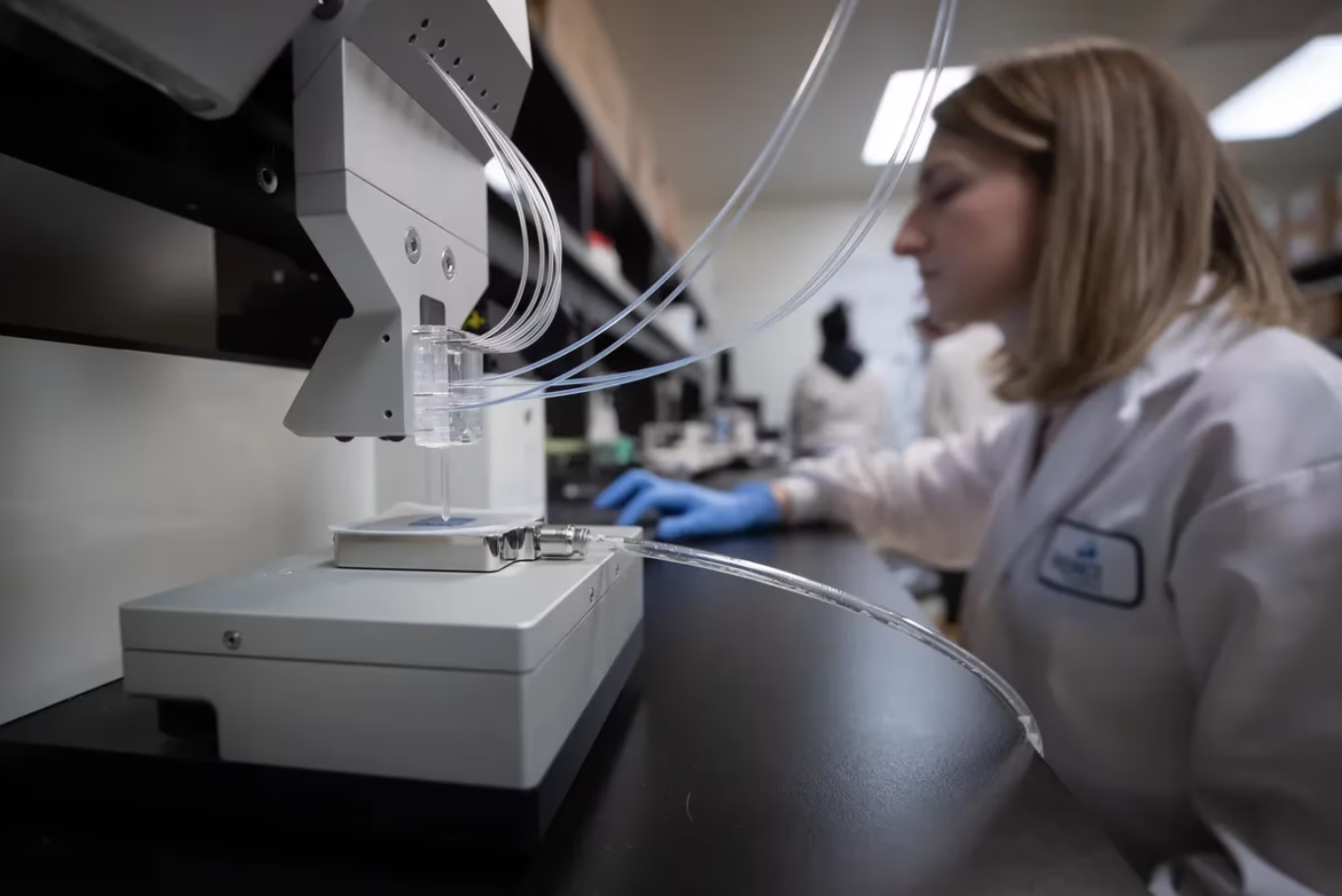
Humanity is now one step closer to realizing Star Trek-esque technology – 3D printing tissue patches to replace impaired biological functions and cure disease. Aspect Biosystems, a Radical Ventures portfolio company, has partnered with Novo Nordisk, a Danish multinational pharma company, to further develop Aspect’s groundbreaking technology. As part of a deal totalling US $2.6 billion in value, Novo Nordisk is paying Aspect US $75 million upfront to fund further research and development on four cell therapy candidates across diabetes and obesity, with each candidate potentially worth $650 million in milestone payments plus royalties.
Aspect’s vision is to build a 3D bioprinting platform that allows scientists to print biological structures that will cure disease. Today, the company combines advanced bio printing with computational design and computer vision to generate implants composed of living cells and tissue-like hydrogel polymers, then prints tissue devices in minutes in a sterile environment. Machine learning is central to scaling this process.
Radical Ventures led Aspect’s Series A round in January 2020, with strong conviction that bio-printed therapeutics would be a new category in regenerative medicine. The transformational partnership with Novo serves as validation that Aspect’s ability to reverse the effect of diseases in areas such as diabetes and obesity opens up the opportunity for additional therapeutic devices.
Aspect sits at the unique intersection of life sciences and Artificial Intelligence, which has the potential to cure diseases in ways that have never before been possible.
AI News This Week
-
The AI 50 2023 (Forbes)
The AI 50 is an annual list in its fifth year recognizing the most promising privately-held companies building businesses out of AI. Collectively, the companies on the 2023 list have received $27.2 billion in funding. This year the list includes Radical Ventures portfolio companies Cohere (providing access to advanced Large Language Models and NLP tools to enterprise), Unlearn (developing a ‘digital twin’ service for clinical trials), and Waabi (creating the next generation of autonomous trucking technology).
-
AI In Space: The amazing ways ML is helping to unravel the mysteries of the universe (Forbes)
AI-assisted machines are being deployed to measure the quality of data from far-off instruments and to improve the efficiency of space telescopes. These machines are also helping to identify and track asteroids and exoplanets, potentially revealing the existence of previously undiscovered planets. Radical Ventures has made two space investments: Pixxel and Muonspace. As space technology continues to advance, the benefits of using AI extend beyond space exploration and into a better understanding of our own planet.
-
Explainer: Building LLM applications for production ( Chip Huyen)
With all of the excitement around open models and APIs there remains a gap between projects and commercially ready tools. The insight from this explainer: it is easy to build something cool with LLMs and it is exceedingly hard to get that cool thing ready for production. A lot of the challenge comes from the ambiguity of natural language, and how to store prompts. The article also includes a list of promising use cases.
-
Developers are connecting multiple AI agents to make more ‘Autonomous’ AI (Motherboard)
Recent large language model experiments aim to create open-source autonomous agents capable of solving various problems via API interaction and other generative agent experiments (see our research spotlight). These agents involving LLMs in recursive loops can fix coding bugs, invent websites, and execute business plans using their “agentic” abilities to perform multiple tasks autonomously and simultaneously. Although primarily suited for small modular modifications, these models require only a detailed description of the problem they need to solve. The agents ask for permission at every step and reveal previous prompts and outcomes to ensure transparency. However, running these programs in “continuous mode” can still cause hallucination and requires extensive calls on the language models’ API.
-
Research Spotlight: Generative Agents: Interactive simulacra of human behaviour (Stanford University/Google Research)
Video games are an exciting category for generative AI offering opportunities to develop agents that combine both language and in-game actions. New research has developed “generative agents” – computer programs that simulate human behavior in video games. These agents can do various activities from cooking breakfast to having conversations with gamers. To make them more realistic, researchers have created an interactive environment that allows users to chat with these agents using natural language. For instance, these agents can plan and host a Valentine’s Day party and invite other agents. The possibilities are varied, making this technology useful not only in video games but also in other interactive applications, including communication tools.
Radical Reads is edited by Leah Morris (Senior Director, Velocity Program, Radical Ventures).